2020 Oscar Nominees Used to Spread Malware
Adam Levin
FEBRUARY 7, 2020
Online scammers are using the 2020 Oscars to spread malware. The post 2020 Oscar Nominees Used to Spread Malware appeared first on Adam Levin.
This site uses cookies to improve your experience. To help us insure we adhere to various privacy regulations, please select your country/region of residence. If you do not select a country, we will assume you are from the United States. Select your Cookie Settings or view our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
Cookies and similar technologies are used on this website for proper function of the website, for tracking performance analytics and for marketing purposes. We and some of our third-party providers may use cookie data for various purposes. Please review the cookie settings below and choose your preference.
Used for the proper function of the website
Used for monitoring website traffic and interactions
Cookies and similar technologies are used on this website for proper function of the website, for tracking performance analytics and for marketing purposes. We and some of our third-party providers may use cookie data for various purposes. Please review the cookie settings below and choose your preference.

Krebs on Security
AUGUST 11, 2020
At least 17 of the bugs squashed in August’s patch batch address vulnerabilities Microsoft rates as “critical,” meaning they can be exploited by miscreants or malware to gain complete, remote control over an affected system with little or no help from users.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Schneier on Security
JANUARY 24, 2022
Crowdstrike is reporting that malware targeting Linux has increased considerably in 2021: Malware targeting Linux systems increased by 35% in 2021 compared to 2020. XorDDoS, Mirai and Mozi malware families accounted for over 22% of Linux-targeted threats observed by CrowdStrike in 2021. Lots of details in the report.

Krebs on Security
JUNE 9, 2020
Eleven of the updates address problems Microsoft deems “critical,” meaning they could be exploited by malware or malcontents to seize complete, remote control over vulnerable systems without any help from users. Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative June 2020 patch lowdown. CERT on Active Exploitation of CVE-2020-0796.

Krebs on Security
NOVEMBER 10, 2020
Some 17 of the 112 issues fixed in today’s patch batch involve “critical” problems in Windows, or those that can be exploited by malware or malcontents to seize complete, remote control over a vulnerable Windows computer without any help from users. “It is very likely he will publish the details of these bugs soon. .

Krebs on Security
MAY 12, 2020
At least 16 of the bugs are labeled “Critical,” meaning ne’er-do-wells can exploit them to install malware or seize remote control over vulnerable systems with little or no help from users. BleepingComputer on May 2020 Patch Tuesday. Further reading: SANS Internet Storm Center breakdown by vulnerability and severity.

Krebs on Security
FEBRUARY 11, 2020
A dozen of the vulnerabilities Microsoft patched today are rated “critical,” meaning malware or miscreants could exploit them remotely to gain complete control over an affected system with little to no help from the user. That vulnerability, assigned as CVE-2020-0674 , has been patched with this month’s release.

Krebs on Security
APRIL 14, 2020
Nineteen of the weaknesses fixed on this Patch Tuesday were assigned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, meaning malware or miscreants could exploit them to gain complete, remote control over vulnerable computers without any help from users. Further reading: Qualys breakdown on April 2020 Patch Tuesday.

Krebs on Security
SEPTEMBER 8, 2020
None of the flaws are known to be currently under active exploitation, but 23 of them could be exploited by malware or malcontents to seize complete control of Windows computers with little or no help from users. “We have seen the previously patched Exchange bug CVE-2020-0688 used in the wild, and that requires authentication. .

Krebs on Security
MARCH 10, 2020
Twenty-six of those earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, meaning malware or miscreants could exploit them to gain complete, remote control over vulnerable computers without any help from users. CVE-2020-0852 is one just four remote execution flaws Microsoft patched this month in versions of Word.

Troy Hunt
JUNE 9, 2021
I've had a couple of cases to date where email addresses compromised by malware then discovered in the course of investigations have been provided to Have I Been Pwned (HIBP). NordLocker has written about the nameless malware that stole 1.2 For guidance on how protecting against malware, read NordLocker's report on the incident.

Krebs on Security
JANUARY 14, 2020
As first reported Monday by KrebsOnSecurity, Microsoft addressed a severe bug ( CVE-2020-0601 ) in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016/19 reported by the NSA that allows an attacker to spoof the digital signature tied to a specific piece of software.
Krebs on Security
JANUARY 13, 2020
14, the first Patch Tuesday of 2020. Such a weakness could be exploited by attackers to make malware appear to be a benign program that was produced and signed by a legitimate software company. Those sources say Microsoft has quietly shipped a patch for the bug to branches of the U.S. Equally concerning, a flaw in crypt32.dll

Tech Republic Security
OCTOBER 11, 2022
Attacks using ATM or PoS malware are on the rise again in 2022 after the COVID-19 lockdowns. The post The 2020-2022 ATM/PoS malware landscape appeared first on TechRepublic.

Schneier on Security
JUNE 30, 2022
Wired is reporting on a new remote-access Trojan that is able to infect at least eighty different targets: So far, researchers from Lumen Technologies’ Black Lotus Labs say they’ve identified at least 80 targets infected by the stealthy malware, including routers made by Cisco, Netgear, Asus, and DrayTek.

Schneier on Security
MAY 18, 2020
A new malware, called Ramsey, can jump air gaps : ESET said they've been able to track down three different versions of the Ramsay malware, one compiled in September 2019 (Ramsay v1), and two others in early and late March 2020 (Ramsay v2.a Seems likely.

Tech Republic Security
APRIL 18, 2024
Nearly 10 million devices were infected with data-stealing malware in 2023, with criminals stealing an average of 50.9 credentials per device.

Penetration Testing
NOVEMBER 27, 2024
This advanced malware exhibits a plethora of customization... The post Elpaco Ransomware: A New Threat Actor Leverages CVE-2020-1472 for Global Attacks appeared first on Cybersecurity News.

Krebs on Security
AUGUST 16, 2020
A security flaw in the way Microsoft Windows guards users against malicious files was actively exploited in malware attacks for two years before last week, when Microsoft finally issued a software update to correct the problem. In fact, CVE-2020-1464 was first spotted in attacks used in the wild back in August 2018.

SecureList
APRIL 23, 2025
We found that the malware was running in the memory of a legitimate SyncHost. Although the exact method by which Cross EX was exploited to deliver malware remains unclear, we believe that the attackers escalated their privileges during the exploitation process as we confirmed the process was executed with high integrity level in most cases.

Krebs on Security
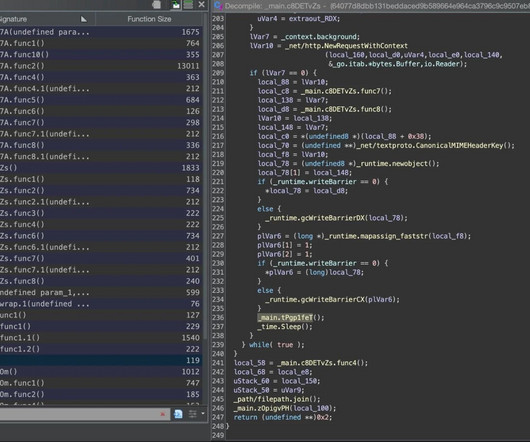
JULY 14, 2020
Top of the heap this month in terms of outright scariness is CVE-2020-1350 , which concerns a remotely exploitable bug in more or less all versions of Windows Server that attackers could use to install malicious software simply by sending a specially crafted DNS request.
Security Affairs
MARCH 26, 2025
New ReaderUpdate malware variants, now written in Crystal, Nim, Rust, and Go, targets macOS users, SentinelOne warns. SentinelOne researchers warn that multiple versions of the ReaderUpdate malware written in Crystal, Nim, Rust, and Go programming languages, are targeting macOS users. The malware maintains persistence via a.plist file.

Schneier on Security
NOVEMBER 20, 2020
The group is using living-off-the-land tools as well as custom malware in this attack campaign, including a custom malware — Backdoor.Hartip — that Symantec has not seen being used by the group before. Cicada has historically been known to target Japan-linked organizations, and has also targeted MSPs in the past.
Krebs on Security
JUNE 1, 2023
This post is a deep dive on “ Megatraffer ,” a veteran Russian hacker who has practically cornered the underground market for malware focused code-signing certificates since 2015. More recently, it appears Megatraffer has been working with ransomware groups to help improve the stealth of their malware. WHO IS MEGATRAFFER?

Tech Republic Security
DECEMBER 23, 2020
Jack Wallen takes one more opportunity to remind Android device owners to use those phones with a great deal of caution; otherwise, they could become victims of malware.

Security Affairs
DECEMBER 27, 2024
charges for allegedly threatening to release data stolen from a company in a March 2020 security breach. government has charged the Brazilian citizen Junior Barros De Oliveira, 29, with allegedly threatening to release data stolen from a company during a March 2020 security breach. A Brazilian citizen faces U.S. Sellinger announced.”

Krebs on Security
AUGUST 14, 2020
It’s unclear when the intruders first breached R1’s networks, but the ransomware was unleashed more than a week ago, right around the time the company was set to release its 2nd quarter financial results for 2020. Sources close to the investigation tell KrebsOnSecurity the malware is known as Defray.
Krebs on Security
FEBRUARY 26, 2023
Web hosting giant GoDaddy made headlines this month when it disclosed that a multi-year breach allowed intruders to steal company source code, siphon customer and employee login credentials, and foist malware on customer websites. But we do know the March 2020 attack was precipitated by a spear-phishing attack against a GoDaddy employee.

Schneier on Security
FEBRUARY 16, 2021
Interesting story about a barcode scanner app that has been pushing malware on to Android phones. But a December 2020 update included some new features: However, a rash of malicious activity was recently traced back to the app. It is baffling to me that an app developer with a popular app would turn it into malware.

Adam Levin
FEBRUARY 8, 2021
An Android app with over 10 million installations spread malware to its users in a recent update. A December 2020 update infected users with a Trojan-style malware that bombards users with unwanted advertising. Barcode Scanner is an app available in the Google Play store for Android devices.
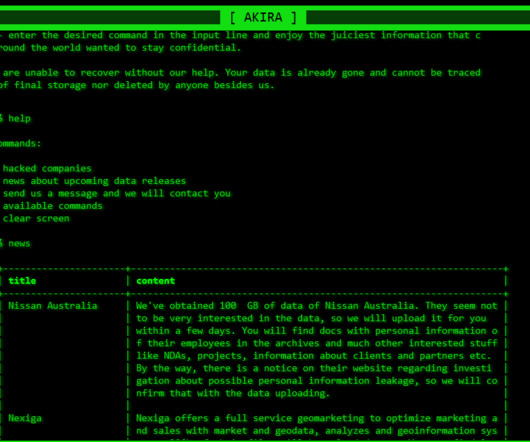
Security Affairs
FEBRUARY 17, 2024
CISA warns that the Akira Ransomware gang is exploiting the Cisco ASA/FTD vulnerability CVE-2020-3259 (CVSS score: 7.5) Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added a Cisco ASA and FTD bug, tracked as CVE-2020-3259 (CVSS score: 7.5), to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog. in attacks in the wild.
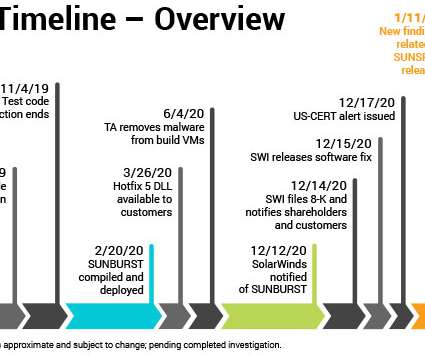
Krebs on Security
JANUARY 12, 2021
New research into the malware that set the stage for the megabreach at IT vendor SolarWinds shows the perpetrators spent months inside the company’s software development labs honing their attack before inserting malicious code into updates that SolarWinds then shipped to thousands of customers. Image: SolarWinds.

Krebs on Security
NOVEMBER 19, 2024
“The threat actor did not deploy malware or tamper with any customer files within the environment,” the notice reads. In March 2020, Finastra suffered a ransomware attack that sidelined a number of the company’s core businesses for days.

Krebs on Security
FEBRUARY 17, 2021
million in a 2018 ATM cash out scheme targeting a Pakistani bank; and a total of $112 million in virtual currencies stolen between 2017 and 2020 from cryptocurrency companies in Slovenia, Indonesia and New York. In reality, prosecutors say, the programs were malware or downloaded malware after the applications were installed.
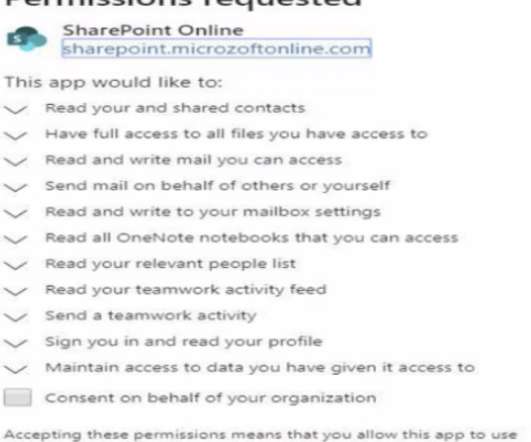
Krebs on Security
MAY 5, 2021
After a user logs in, the link prompts them to install a malicious but innocuously-named app that gives the attacker persistent, password-free access to any of the user’s emails and files, both of which are then plundered to launch malware and phishing scams against others.
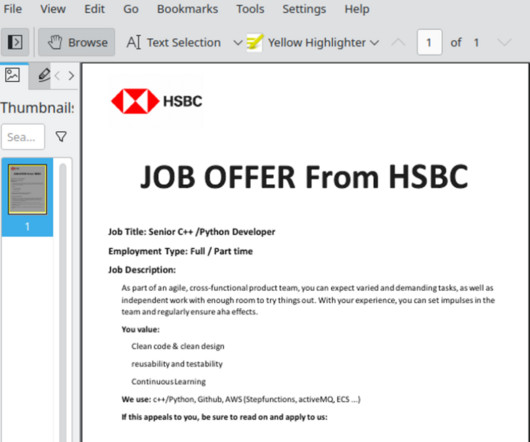
Krebs on Security
APRIL 20, 2023
Researchers at ESET say this job offer from a phony HSBC recruiter on LinkedIn was North Korean malware masquerading as a PDF file. Mandiant found the compromised 3CX software would download malware that sought out new instructions by consulting encrypted icon files hosted on GitHub. Image: Mandiant.

The Last Watchdog
APRIL 21, 2021
From January through March 2021, TLS concealed 45 percent of the malware Sophos analysts observed circulating on the Internet; that’s double the rate – 23 percent – seen in early 2020, Dan Schiappa, Sophos’ chief product officer, told me in a briefing. And then they may use off-the-shelf malware to carry out their attack.
Security Affairs
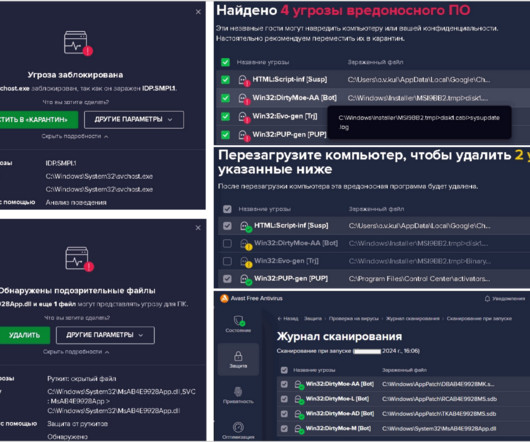
FEBRUARY 2, 2024
The Computer Emergency Response Team in Ukraine (CERT-UA) reported that a PurpleFox malware campaign had already infected at least 2,000 computers in the country. Experts defined DirtyMoe as a complex malware that has been designed as a modular system. ” reads the alert published by CERT-UA.

Krebs on Security
DECEMBER 16, 2020
13, cyber incident response firm FireEye published a detailed writeup on the malware infrastructure used in the SolarWinds compromise, presenting evidence that the Orion software was first compromised back in March 2020. ” The statement continues: “Depending on the IP address returned when the malware resolves avsvmcloud[.]com,
Security Affairs
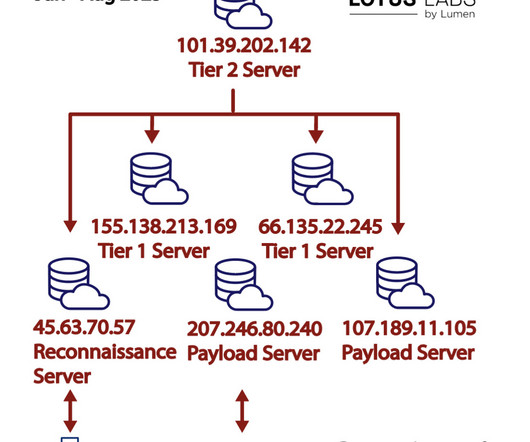
DECEMBER 17, 2024
The FBI warned of a fresh wave of HiatusRAT malware attacks targeting internet-facing Chinese-branded web cameras and DVRs. The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) released a Private Industry Notification (PIN) to warn of HiatusRAT malware campaigns targeting Chinese-branded web cameras and DVRs. ” reads the PIN report.

Krebs on Security
MARCH 20, 2020
This week, security researchers said they spotted that same vulnerability being exploited by a new variant of Mirai , a malware strain that targets vulnerable Internet of Things (IoT) devices for use in large-scale attacks and as proxies for other cybercrime activity. A joint advisory on CVE-2020-9054 from the U.S.

Krebs on Security
APRIL 18, 2022
” On April 13, Microsoft said it executed a legal sneak attack against Zloader , a remote access trojan and malware platform that multiple ransomware groups have used to deploy their malware inside victim networks. alone by October 2020.

Malwarebytes
OCTOBER 18, 2024
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-44133 was fixed in the September 16 update for Mac Studio (2022 and later), iMac (2019 and later), Mac Pro (2019 and later), Mac Mini (2018 and later), MacBook Air (2020 and later), MacBook Pro (2018 and later), and iMac Pro (2017 and later).
Expert insights. Personalized for you.
We have resent the email to
Are you sure you want to cancel your subscriptions?



Let's personalize your content