UK Ad Campaign Seeks to Deter Cybercrime
Krebs on Security
MAY 28, 2020
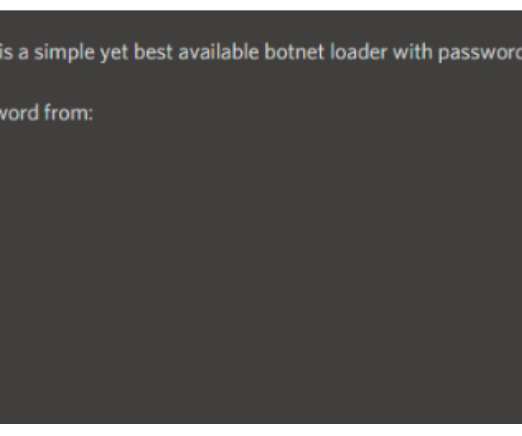
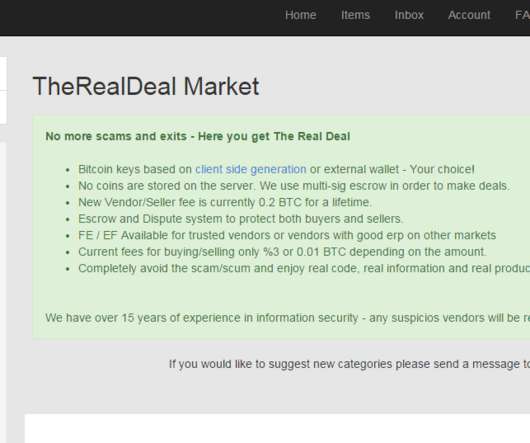
The United Kingdom’s anti-cybercrime agency is running online ads aimed at young people who search the Web for services that enable computer crimes, specifically trojan horse programs and DDoS-for-hire services. ’s National Crime Agency , which saw success with a related campaign for six months starting in December 2017.







































Let's personalize your content